The advent of 5G technology marks a significant turning point in global communications. With unprecedented speeds and reduced latency, this technology is set to revolutionize the way we connect and interact online. From faster downloads to seamless video streaming, 5G is transforming digital experiences like never before.
Beyond personal connectivity, 5G technology are driving innovation across multiple industries. Healthcare will benefit from real-time remote consultations, while autonomous vehicles and smart cities will rely on its ultra-fast data transmission. Businesses, too, will experience enhanced productivity with more efficient cloud computing and IoT integration.
As 5G continues to expand, its impact will only grow stronger. Understanding its full potential is key to staying ahead in an increasingly connected world. Keep reading to explore how 5G technology are shaping the future and what this means for different industries.
Understanding 5G Technology
5G technology is the fifth generation of mobile communication, designed to be faster and more efficient than its predecessors. Unlike 4G, which primarily focuses on enhancing mobile broadband, 5G aims to connect a variety of devices, catering to the Internet of Things (IoT). This means that everything from smart home devices to autonomous vehicles can communicate with one another seamlessly.
Key Features of 5G
One of the standout features of 5G networks is their ability to offer higher data speeds, predicted to be up to 100 times faster than 4G. This creates opportunities for real-time applications, like remote surgery and virtual reality experiences. Additionally, 5G has a lower latency, which means less delay in communication – crucial for applications where timing is critical.
How 5G Works
5G technology operates using a mixture of lower and higher frequency radio waves, which allows for more data to be transmitted at once. The technology utilizes small cell stations to reduce the distance data needs to travel, enhancing speed and efficiency. These small cells are essential for maintaining the performance of 5G in densely populated areas where traditional towers may struggle to provide adequate coverage.
Real-World Applications of 5G
The impact of 5G networks transcends just faster internet speeds. It has the potential to revolutionise industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. For instance, telemedicine could become more accessible with seamless video consultations and remote monitoring of patients. In manufacturing, 5G could enable factories to implement smarter and more automated production lines.
Security Considerations
As with any advancement in technology, security is a critical consideration for 5G. With increased connectivity comes the risk of cyber threats. It is vital for stakeholders to invest in robust security measures to safeguard their networks against potential attacks.
Key Components of 5G Networks
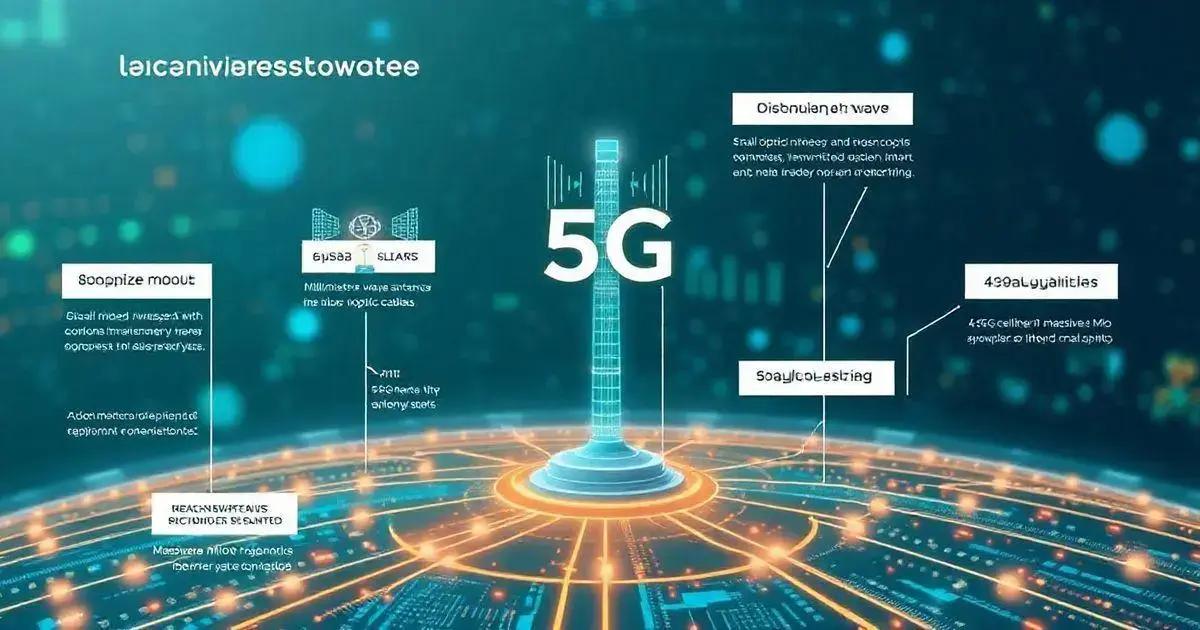
Key components of 5G networks are essential for delivering high-speed, low-latency communications. Understanding these components helps us appreciate how 5G technology works and its global impact.
Small Cells
Small cells are vital for 5G networks, as they provide coverage in densely populated areas. These small base stations can be placed on streetlights or buildings to enhance connectivity without the need for large towers. They help maintain strong signals and support the high frequency of 5G technology.
MIMO Technology
Massive MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output) is another critical element. This technology uses multiple antennas to send and receive more data at once, improving capacity and efficiency. By increasing the number of connections, massive MIMO enables more users to access the network simultaneously without slowdowns.
Millimetre Waves
5G networks utilise millimetre wave frequencies, which allow for greater data transmission speeds. These high-frequency bands can carry vast amounts of information and are necessary for the ultra-fast internet speeds promised by 5G technology. However, they have shorter ranges and require more small cells to ensure coverage.
Fiber Optic Cables
In order to connect these components effectively, 5G networks rely on fiber optic cables for backhaul. These cables transmit data at high speeds over long distances, ensuring a stable connection between the small cells and the core network.
Beamforming
Beamforming technology directs signals towards specific users rather than broadcasting in all directions. This improves the signal strength and quality for end-users, dramatically enhancing connectivity and reducing interference.
Network Slicing
Network slicing allows operators to create multiple virtual networks within a single physical 5G network. This caters to different needs, such as autonomous vehicles, smart homes, or industrial applications, ensuring each has the required resources and performance levels.
Global Adoption of 5G
Global adoption of 5G is rapidly increasing, with many countries investing heavily in this technology. As 5G networks become more available, various sectors are looking to leverage their benefits. Countries like South Korea, China, and the United States are leading the charge in deploying 5G technology.
Regional Leaders in 5G
South Korea was among the first to launch a nationwide 5G network, offering services to its citizens as early as 2019. In China, the government aims to cover most major cities with 5G by 2025, influencing numerous industries. The United States has also made significant strides, with major telecom companies rolling out 5G networks across the country.
Growth in Subscriptions
The number of 5G subscriptions worldwide is projected to grow rapidly. By 2025, analysts predict that there will be over 1.7 billion 5G users. This impressive growth is fuelled by the desire for faster internet speeds and better connectivity.
Impact on Industries
As 5G networks expand globally, various industries are poised to benefit. Sectors such as healthcare are exploring the use of 5G technology for telemedicine, allowing doctors to consult with patients remotely. Likewise, the automotive industry is investing in 5G for connected and autonomous vehicles that require real-time data processing.
Barriers to Global Adoption
Despite its advantages, global adoption of 5G faces challenges like infrastructure costs and regulatory hurdles. Many countries need to upgrade their existing infrastructure to support 5G technology. Additionally, there are concerns over security and potential health effects that need addressing.
The Future of 5G Adoption
As we look into the future, the race for 5G networks will likely intensify. Countries that invest early in 5G technology will potentially gain a competitive edge. The benefits of 5G are expected to transform economies and improve the way we live and work.
5G Networks and Economic Growth
5G networks are set to significantly boost economic growth on a global scale. As countries implement 5G technology, they create opportunities for innovation across various industries, leading to job creation and increased productivity.
Enhancing Business Operations
With faster and more reliable internet access, businesses can streamline operations. Enhanced connectivity allows for improved communication, better collaboration, and more efficient processes. Companies can implement advanced technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and IoT, which rely on strong internet infrastructure provided by 5G networks.
Job Creation
The rollout of 5G networks creates numerous jobs in sectors such as telecommunications, construction, and technology. As 5G expands, the demand for skilled workers will increase, giving a boost to the economy. This labour market expansion can benefit local communities, providing more opportunities for employment.
Investment in Infrastructure
Countries investing in 5G infrastructure are likely to see additional foreign investments. The creation of modernized technologies attracts businesses looking to collaborate and innovate. This influx of investment can lead to economic growth and increased competitiveness.
Boosting Industries
Industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and transport are expected to see substantial improvements due to 5G networks. In healthcare, for instance, telemedicine can thrive, allowing doctors to connect with patients remotely. In transportation, 5G technology can enhance the development of smart cities with connected vehicles, improving efficiency and safety.
Long-Term Economic Impact
The long-term economic impact of 5G networks is projected to be significant. As countries continue to invest in this technology, they can expect a wave of economic activity. Reports suggest that 5G could contribute trillions of dollars to the global economy by driving advancements in diverse sectors.
Impact of 5G on Health and Environment
The introduction of 5G networks brings many changes, and its impact on health and the environment are important topics of discussion. With advanced technology, we can examine both potential benefits and concerns.
Potential Health Concerns
One primary concern regarding 5G technology is its exposure to radiofrequency (RF) radiation. While existing research suggests that 5G emits radiation at levels similar to those of previous generations, some individuals worry about the long-term effects. Ongoing studies aim to better understand the potential health effects of increased exposure.
Regulatory Standards
Regulatory bodies such as the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) provide guidelines on safe exposure levels to RF radiation. These standards are instrumental in ensuring that the rollout of 5G networks is safe for the public and the environment.
Environmental Impact of Infrastructure
The deployment of 5G networks requires infrastructure changes, including the installation of more small cell towers. This can lead to urban development and changes in land use. While this infrastructure supports advanced technology, it is essential to consider its effect on wildlife habitats and local ecosystems.
Energy Efficiency
One of the benefits of 5G technology is its potential for energy efficiency. Compared to older generations, 5G networks are designed to use resources more effectively. This can lead to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions associated with data transmission.
Smart Solutions for the Environment
Another positive impact of 5G is its application in environmental monitoring. With enhanced connectivity, sensors can be deployed to track air quality, water levels, and wildlife movements. These data insights can contribute to better environmental management.
5G and Its Role in Smart Cities

5G networks play a crucial role in the development of smart cities, enhancing the quality of life for residents through improved technology and connectivity. As urban areas grow, the need for efficient infrastructure and communication becomes essential.
Improved Connectivity
With 5G technology, smart cities can connect various devices and systems seamlessly. This allows for better communication between vehicles, traffic lights, and public transport, resulting in smoother transportation and less congestion.
Smart Transportation
The integration of 5G into transportation systems promotes smart solutions like traffic management and autonomous vehicles. Real-time data can help manage traffic flows, reduce delays, and even enhance safety for pedestrians and drivers alike.
Energy Management
5G networks enable smart meters and devices that can optimise energy usage in buildings. By connecting these devices, cities can reduce waste and improve their energy efficiency. This leads to lower costs and a more sustainable environment.
Public Safety Enhancements
Through 5G technology, emergency services can respond faster to incidents. Real-time data sharing between police, fire departments, and hospitals can improve response times and coordination during emergencies, ultimately saving lives.
Environmental Monitoring
Smart cities can use 5G networks to monitor environmental conditions more effectively. Sensors can collect data on air quality, noise levels, and waste management. This information can help cities make informed decisions about public health and urban planning.
Citizen Engagement
With enhanced connectivity, residents can engage more easily with their local governments. Mobile applications powered by 5G technology can provide citizens with access to services, information, and opportunities to participate in community planning.
Challenges in 5G Implementation
The implementation of 5G networks comes with various challenges that need to be addressed for successful deployment. These challenges can hinder the efficiency and effectiveness of the technology.
Infrastructure Costs
One major challenge is the high cost of infrastructure. Deploying 5G technology requires substantial investment in new equipment, such as small cells, fiber optics, and antennas. Many countries and companies may struggle to allocate the necessary funds to build out the infrastructure.
Regulatory Hurdles
Regulatory issues also impact the speed of 5G implementation. Different countries have different regulations surrounding telecommunications. Navigating these laws can be complex and may delay the rollout of 5G networks.
Geographical Challenges
Geographical factors can pose difficulties in deploying 5G technology. In urban areas, high-density structures can interfere with signals. In rural areas, the sparse population makes it less profitable to install the required infrastructure.
Security Concerns
With the introduction of 5G networks, there are significant security concerns. These networks can be more vulnerable to cyberattacks due to their complex nature and the increased number of connected devices. Ensuring cybersecurity will be essential for maintaining trust and safety.
Public Misconceptions
Public perception and misconceptions around 5G technology can also be a challenge. Some people have concerns about the health effects of 5G radiation, which may lead to resistance against the infrastructure installation. Effective communication about safety measures and the benefits of 5G is crucial.
Technical Challenges
Technical challenges regarding interoperability can impact the functionality of 5G networks. Ensuring that new technologies work seamlessly with existing infrastructure is necessary for a smooth transition to 5G.
Future Trends in 5G Networks
Future trends in 5G networks are central to understanding how this technology will evolve and impact our lives. As innovation continues, the following trends are expected to shape the future of 5G technology.
Increased Adoption of IoT
One major trend is the rapid growth of the Internet of Things (IoT). With 5G networks, more devices will connect to the internet, allowing everything from smart home devices to industrial equipment to communicate efficiently. This increased connectivity will enable smarter homes and businesses.
Enhanced Mobile Experience
The future of 5G will bring improvements in mobile experiences. Users can expect faster download speeds, lower latency, and seamless video streaming. This enhanced mobile experience will revolutionise how we interact with content, whether through gaming, streaming, or virtual reality.
Expanded Applications in Healthcare
Healthcare will see significant advancements as 5G networks become more widespread. Telemedicine will improve with high-quality video consultations and remote monitoring tools. This means doctors can provide better care to patients without needing physical appointments.
Smart City Developments
As cities continue to grow, 5G technology will lead to the development of smart cities. This includes everything from smart traffic management systems to efficient public transportation, reducing congestion and improving urban living.
Advanced Security Measures
Future 5G networks will likely incorporate enhanced security features to counteract increasing cyber threats. Telecommunications providers will need to develop robust security protocols to protect data and maintain user trust.
Network Slicing
Network slicing will be an important aspect of 5G technology as it allows operators to create multiple virtual networks within a single physical 5G network. This means different services can operate smoothly, catering to various user needs, from emergency services to regular consumer applications.
Understanding the global impact of 5G networks
5G networks represent a significant leap in communication technology, likely transforming various aspects of our daily lives and the global economy. As we explored, the key components and trends of 5G technology highlight its potential in fostering economic growth and enhancing smart city initiatives.
However, along with these benefits, challenges such as implementation costs, regulatory hurdles, and public perception must be navigated carefully. Addressing these concerns will be crucial to fully realise the opportunities that 5G networks offer.
Ultimately, as we witness the advancement of 5G, it is essential for stakeholders—from governments and corporate entities to individuals—to collaborate and innovate, ensuring that this revolutionary change is beneficial for all.
Check out our article on Emerging Technologies to discover how new innovations are shaping industries and revolutionizing the way we live and work.
